Cross-Modal Sensory Information Integration in Modulation of Vertebrate Visual System Functions
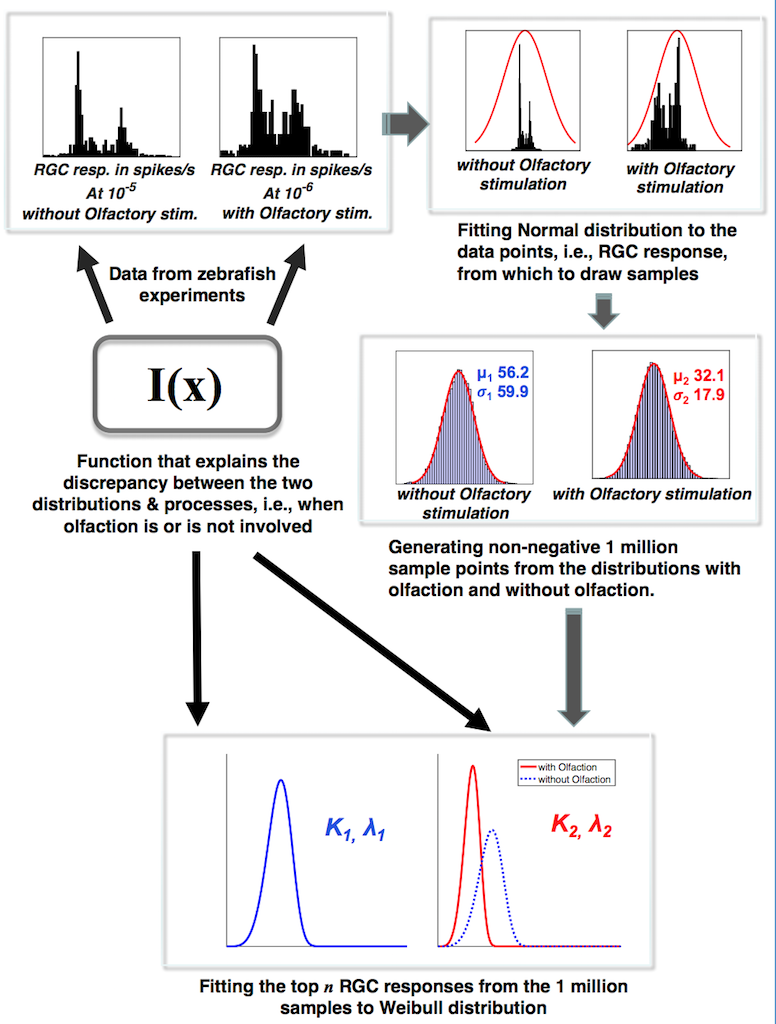
In this project, we investigate the cross-modal signaling interactions between different sensory systems, specifically the centrifugal signals in modulation of the visual system, in zebrafish. They originate in the Terminalis Neuron (TN) that is housed in the Olfactory Bulb (OB). Naturally, olfaction influences vision in zebrafish. Based on the results from wet-bench experiments examining the above circuit-level phenomena, we are working towards computational neural models that leverage the principles of the statistical extreme value theory (EVT) to simulate and predict the consequence of sensory integration in retinal function.
[poster]